Friday, April 10, 2009
Malta’s Three Cities are Senglea, Victorioso and Conspicua. The first is named after Grandmaster Claude de la Sengle. The second and third are
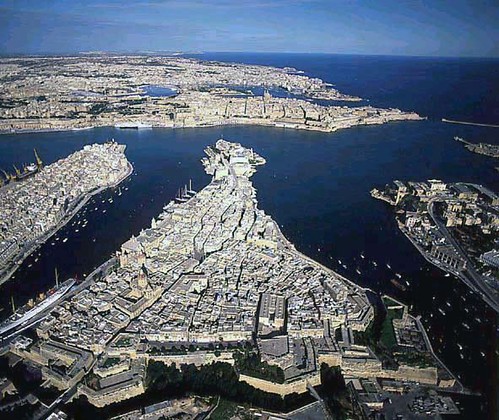

nods to the victorious Knights of St. John and the 1565 siege of Malta, that titanic event in Maltese history that pitted Mustapha Pasha, commander of the Turkish land forces and Piale Pasha, commander of the Turkish navy, against Jean Parisot de la Valette, 48th Grandmaster of the Knights of St. John. Malta’s capital city, Valetta, is named after him. His portrait hangs in the throne room of the Grandmaster’s palace. In it he is wearing an outer garment that looks like the Maltese flag with sleeves.
Malta’s written history begins with the Phoenicians, who inhabited the island around 800BC. It was a whipping post during the Punic Wars, finally ending up in the hands of the Romans until the dissolution of the Roman Empire. Then it changed hands like a hot potato, Byzantines, Arabs, Normans, the Spanish. King James the First of Aragon expelled all the Muslims on the island around the year 1250AD. The Spanish were always expelling someone, Arabs, Muslims, Jews—and always to their own detriment since in every case it put their economic clock back at least a hundred years. In 1530 Charles V offered Malta to the Knights of St. John. The locals didn’t have a say in the matter. Charles was looking for a cheap first line of defense against the Turks.
The great siege began on the 23 of May 1565 with an attack on Fort St. Elmo. Suleyman the Magnificent was intent on using Malta as a stepping-stone to Sicily and then Europe.He sent a land and a sea force to do the job. The Ottoman naval attack was under the command of Dragut, the 80 year old commander who, fourteen years earlier, in 1551 had defeated the very same Knights at the Battle of Tripoli. After a month of remorseless bombardment, Fort St. Elmo succumbed, but not before a cannonball put an end to the old man himself. News of St. Elmo’s fall reached Dragut just moments before he died. He is reported to have made several signs of joy, including raising his eyes heavenward “as if in thankfulness for its mercies.” Then he closed them forever. At his death Mustapha Pasha, commander of the land forces that suffered a loss of 8,000 men, is recorded as having said, “If so small a son has cost us so dear, what price must we pay for the father.” By the son he meant St. Elmo. The father, of course, was Fort St. Angelo.
What interests me about this battle is the way in which the two leaders, Jean de la Valette and Dragut, the one a seventy one year old Christian, the other an 80 year old Muslim, announced their intention to fight to the death.
Upon breaching the walls of St. Elmo’s, Mustapha Pasha found 60 Knights of St. John’s still alive out of the original force of roughly 150. He promptly decapitated all of them save nine. (I wonder why nine and not one for each apostle.) These he nailed to wooden crosses in mockery of the crucifixion and sent them floating, crosses and all, across the harbor to St. Angelo’s. De la Valette showed that he, too, had an imagination the equal of Mustapha Pasha’s. He decapitated all his Turkish prisoners, stuffed their heads into cannon and fired them back across the harbor to St. Elmo’s.
The battle was one of the most momentous not only in Maltese history, but in the history of Europe itself. Here is Jean de la Valette bravely holding out against the Turks for three and a half months.
Nor could he have held out much longer. Fortunately for him, the Grand Viceroy of Sicily sent 9,000 men to the rescue. This was the so-called Grand Soccorso. There is a frieze commemorating it in the throne room at the Grandmaster’s palace. This relief force was enough to send Piale Pascha and his brother Mustapha back to Suleyman the Magnificent with a shrug of their shoulders that said, “Not this time.” Suleyman said, “With me alone do my armies triumph.” He, too, was an old man.
More than 12,000 men died in this battle including 400 Knights of St. John and yet the image of octogenarian Dragut sending nine crucified Knights floating toward de la Valette and the septuagenarian de la Valette retaliating by stuffing cannon with the heads of dead Turks and sky-rocking them back to Dragut strikes me as, well, if not funny, at least blood-curdlingly ridiculous. What would they have done if they had been forced to face one another directly? Claw at one another’s beards? Stomp petulantly on the ground until one of them died of apoplexy? I am awestruck at the endlessly creative ways mankind, especially old mankind, has devised to kill off its young men.
I look out over the waters of Dockyard Creek at St. Angelo and Senglea and count the expensive yachts moored to the quays. I watch the tiny tourist boats skittering beneath the citadels like water spiders. As I look at the brand new condos, still unfilled, whose balconies overlook the four hundred and forty four year old slaughterhouse of St. Elmo’s, each condo costing at least 700,000 Euros for 800 square meters of space, it is hard for me to see the history of what happened here as anything other than absurd. But that, I suppose, makes it no different from any other conflict in the history of the world, a history in which men have chosen to resolve their differences by killing their adversaries instead of their impulses.
Malta is not so much an island as it is the top of a mountain. Some 14,000 years ago the glacier that covered Europe began to recede. As it did, the water level of the Mediterranean rose, some 120 meters to be exact, enough, anyway, to separate Malta from its mainland. Just 80 kilometers separates the island from Sicily’s Cape Passero. On a clear day you can see Mt. Etna.
The first inhabitants reached Malta around 5200BC, roughly 2500 years before the building of the Palace of King Minos at Knossus. The oldest free standing stone structures in the world are here. They date from 4000BC to 2500BC. These structures belong to the so-called Temple period. They were not dwellings but ceremonial buildings in which god knows what went on. Orgies, maybe. Or sun worship. Or just plain old gossip mongering. We don’t know who the people were or where they came from, except that it was probably over water from Sicily.
If you were to take these corpulent figures and stretch them out like pieces of salt water taffy, so that the legs are no longer massive but straight limbed and leave the arms folded across the stomach just the way we see them now, you would have the typical figures found in the Cyclades, those islands at the mouth of the Aegean Sea.
There is one exception to this notion that the ancients were as good as any of us. I am thinking of the ability of sculptors to present the human figure realistically. That didn’t happen, as far as I can see, until 600 BC around the time of Phidias and the Parthenon. Michaelangelo and Bernini brought it to its highest level in the 15th century AD. Indeed, Michelangelo’s Pietà has my vote for the world’s greatest statue. In any event realism took about 2100 years to emerge. From then on it has been same old, same old.
When I first arrived in Malta, I had a strong feeling of déjà vu. But I knew that was impossible. Then I realized what it was. I’d seen the Da Vinci Code and Swept Away and Gladiator and Troy. They were all made here.
I think that if I had to live on Malta I would go stir crazy. The island is 18 miles long and nine miles wide. Nothing is more than an hour’s drive from anything else and most of that time is spent in traffic. Aside from the monuments like the Co-Cathedral of St. John where, by the way, John de la Valette is buried and the Grandmaster’s
palace and the forts and the monumental fortifications and the walled city of Mdina, I get the feeling that Malta is either an unattractive slather of cheap concrete tenements, or a very expensive summer home for the wealthy.
Some of the yachts moored in Dockyard Creek looked as if they could launch another attack on St. Elmo’s. How viable is a society like this, especially during the current global economic crisis? The rich come in for a couple of months, bask in the sun and then hop it for wherever they keep their money while the native Maltese watch them come and go and wonder whether this is just one more wave of invaders like the Romans, the Byzantines, the Arabs and the Normans.
It would be nice to spend a year here so that I could see if what I sense is really true. But then it would be nice to spend a year in Rio de Janeiro or Rome or Kyoto. Who has the time? I’m already too old to drive in Malta.
Malta’s written history begins with the Phoenicians, who inhabited the island around 800BC. It was a whipping post during the Punic Wars, finally ending up in the hands of the Romans until the dissolution of the Roman Empire. Then it changed hands like a hot potato, Byzantines, Arabs, Normans, the Spanish. King James the First of Aragon expelled all the Muslims on the island around the year 1250AD. The Spanish were always expelling someone, Arabs, Muslims, Jews—and always to their own detriment since in every case it put their economic clock back at least a hundred years. In 1530 Charles V offered Malta to the Knights of St. John. The locals didn’t have a say in the matter. Charles was looking for a cheap first line of defense against the Turks.
The great siege began on the 23 of May 1565 with an attack on Fort St. Elmo. Suleyman the Magnificent was intent on using Malta as a stepping-stone to Sicily and then Europe.He sent a land and a sea force to do the job. The Ottoman naval attack was under the command of Dragut, the 80 year old commander who, fourteen years earlier, in 1551 had defeated the very same Knights at the Battle of Tripoli. After a month of remorseless bombardment, Fort St. Elmo succumbed, but not before a cannonball put an end to the old man himself. News of St. Elmo’s fall reached Dragut just moments before he died. He is reported to have made several signs of joy, including raising his eyes heavenward “as if in thankfulness for its mercies.” Then he closed them forever. At his death Mustapha Pasha, commander of the land forces that suffered a loss of 8,000 men, is recorded as having said, “If so small a son has cost us so dear, what price must we pay for the father.” By the son he meant St. Elmo. The father, of course, was Fort St. Angelo.
What interests me about this battle is the way in which the two leaders, Jean de la Valette and Dragut, the one a seventy one year old Christian, the other an 80 year old Muslim, announced their intention to fight to the death.
Upon breaching the walls of St. Elmo’s, Mustapha Pasha found 60 Knights of St. John’s still alive out of the original force of roughly 150. He promptly decapitated all of them save nine. (I wonder why nine and not one for each apostle.) These he nailed to wooden crosses in mockery of the crucifixion and sent them floating, crosses and all, across the harbor to St. Angelo’s. De la Valette showed that he, too, had an imagination the equal of Mustapha Pasha’s. He decapitated all his Turkish prisoners, stuffed their heads into cannon and fired them back across the harbor to St. Elmo’s.
The battle was one of the most momentous not only in Maltese history, but in the history of Europe itself. Here is Jean de la Valette bravely holding out against the Turks for three and a half months.
Nor could he have held out much longer. Fortunately for him, the Grand Viceroy of Sicily sent 9,000 men to the rescue. This was the so-called Grand Soccorso. There is a frieze commemorating it in the throne room at the Grandmaster’s palace. This relief force was enough to send Piale Pascha and his brother Mustapha back to Suleyman the Magnificent with a shrug of their shoulders that said, “Not this time.” Suleyman said, “With me alone do my armies triumph.” He, too, was an old man.
More than 12,000 men died in this battle including 400 Knights of St. John and yet the image of octogenarian Dragut sending nine crucified Knights floating toward de la Valette and the septuagenarian de la Valette retaliating by stuffing cannon with the heads of dead Turks and sky-rocking them back to Dragut strikes me as, well, if not funny, at least blood-curdlingly ridiculous. What would they have done if they had been forced to face one another directly? Claw at one another’s beards? Stomp petulantly on the ground until one of them died of apoplexy? I am awestruck at the endlessly creative ways mankind, especially old mankind, has devised to kill off its young men.
I look out over the waters of Dockyard Creek at St. Angelo and Senglea and count the expensive yachts moored to the quays. I watch the tiny tourist boats skittering beneath the citadels like water spiders. As I look at the brand new condos, still unfilled, whose balconies overlook the four hundred and forty four year old slaughterhouse of St. Elmo’s, each condo costing at least 700,000 Euros for 800 square meters of space, it is hard for me to see the history of what happened here as anything other than absurd. But that, I suppose, makes it no different from any other conflict in the history of the world, a history in which men have chosen to resolve their differences by killing their adversaries instead of their impulses.
Malta is not so much an island as it is the top of a mountain. Some 14,000 years ago the glacier that covered Europe began to recede. As it did, the water level of the Mediterranean rose, some 120 meters to be exact, enough, anyway, to separate Malta from its mainland. Just 80 kilometers separates the island from Sicily’s Cape Passero. On a clear day you can see Mt. Etna.
The first inhabitants reached Malta around 5200BC, roughly 2500 years before the building of the Palace of King Minos at Knossus. The oldest free standing stone structures in the world are here. They date from 4000BC to 2500BC. These structures belong to the so-called Temple period. They were not dwellings but ceremonial buildings in which god knows what went on. Orgies, maybe. Or sun worship. Or just plain old gossip mongering. We don’t know who the people were or where they came from, except that it was probably over water from Sicily.
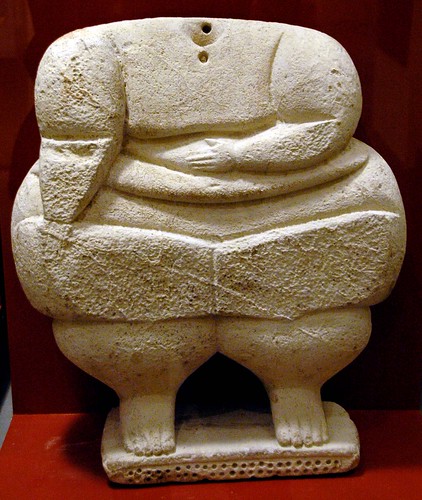
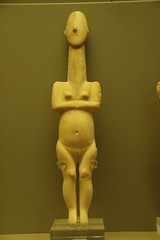
We have fragments of their art; Temple art, those concupiscent female figures with their arms folded across their fat bellies and their thighs bulging like weather balloons. Botero could easily have sculpted these figures. Or rather Botero could easily have made his reputation by copying them.
If you were to take these corpulent figures and stretch them out like pieces of salt water taffy, so that the legs are no longer massive but straight limbed and leave the arms folded across the stomach just the way we see them now, you would have the typical figures found in the Cyclades, those islands at the mouth of the Aegean Sea.
I’m not sure what this all this means—the Temple figures, the Cycladic figures, Botero—except to say that when it comes to artistic intelligence there really is nothing new under the sun. Every age has had its geniuses. The only thing that has changed is the technology that allows the same ideas to be expressed in difference ways. As far as I am concerned, the Templatic sculptures of Hagar Qim are as good as any piece of abstract sculpture on the market today.
There is one exception to this notion that the ancients were as good as any of us. I am thinking of the ability of sculptors to present the human figure realistically. That didn’t happen, as far as I can see, until 600 BC around the time of Phidias and the Parthenon. Michaelangelo and Bernini brought it to its highest level in the 15th century AD. Indeed, Michelangelo’s Pietà has my vote for the world’s greatest statue. In any event realism took about 2100 years to emerge. From then on it has been same old, same old.
When I first arrived in Malta, I had a strong feeling of déjà vu. But I knew that was impossible. Then I realized what it was. I’d seen the Da Vinci Code and Swept Away and Gladiator and Troy. They were all made here.
I think that if I had to live on Malta I would go stir crazy. The island is 18 miles long and nine miles wide. Nothing is more than an hour’s drive from anything else and most of that time is spent in traffic. Aside from the monuments like the Co-Cathedral of St. John where, by the way, John de la Valette is buried and the Grandmaster’s
palace and the forts and the monumental fortifications and the walled city of Mdina, I get the feeling that Malta is either an unattractive slather of cheap concrete tenements, or a very expensive summer home for the wealthy.
Some of the yachts moored in Dockyard Creek looked as if they could launch another attack on St. Elmo’s. How viable is a society like this, especially during the current global economic crisis? The rich come in for a couple of months, bask in the sun and then hop it for wherever they keep their money while the native Maltese watch them come and go and wonder whether this is just one more wave of invaders like the Romans, the Byzantines, the Arabs and the Normans.
It would be nice to spend a year here so that I could see if what I sense is really true. But then it would be nice to spend a year in Rio de Janeiro or Rome or Kyoto. Who has the time? I’m already too old to drive in Malta.